Does Finasteride Work for Hair Loss in Women?
Key takeaways:
Finasteride (Propecia) works by preventing testosterone from turning into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which lessens the amount of DHT in the body. DHT is a hormone that is linked to hair loss in women and men.
Finasteride is an effective treatment for hair loss in men at 1 mg per day. Finasteride at 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg per day might also work for hair loss in women.
Finasteride may cause birth defects, so pre-menopausal women should use a reliable birth control method when taking finasteride. Also, talk with your healthcare provider if you suspect that you’re pregnant.

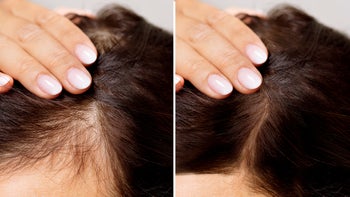
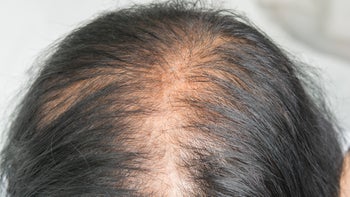
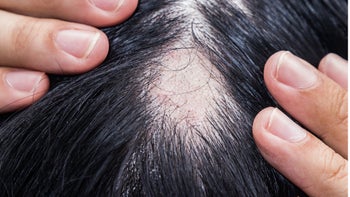
Many people experience hair shedding. As you get older, you may also notice some changes in the color and thickness of your hair. But some people might have excessive alopecia (hair loss) that can be distressing and impact quality of life.
There are many different types or causes of hair loss. If you experience hair loss, talk with your healthcare provider to find out what’s causing your hair loss. The most common type of hair loss is androgenetic or androgenic alopecia, which affects around 50 million men and 30 million women in the U.S. This common hair condition is also known as male pattern hair loss in men and female pattern hair loss in women.
Fortunately, there are treatments available for hair loss. One common option is finasteride (Propecia). In this article, we’ll talk more about finasteride — how it works, how effective it is, and what side effects to expect.
How does finasteride work for hair loss?
Finasteride works for hair loss by stopping testosterone from turning into DHT (dihydrotestosterone). As a result, the amount of DHT in the body becomes lower. DHT is a hormone that is linked to hair loss in both women and men.
The downside is that finasteride is also teratogenic — meaning that if you get pregnant while taking it, it may cause negative effects to your unborn baby. For this reason, premenopausal women should use a reliable form of birth control while taking finasteride. And pregnant women shouldn’t take finasteride.
Are there side effects of Finasteride that affect both men and women?
In short, yes. Men and women may experience the following side effects with finasteride:
Dizziness
Low sexual desire (libido)
Breast swelling
Breast tenderness
How long can you take finasteride to treat hair loss?
To treat hair loss, you will need to take finasteride long-term. If you stop taking this medication, you’ll start to lose your hair again.
What dosage of finasteride works for men?
For male pattern hair loss, the FDA approved finasteride at a daily dose of 1 mg. But the daily finasteride dose is higher at 5 mg in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In BPH, an enlarged prostate can cause symptoms like a weak urine stream or more urgent need to use the restroom.
How effective is finasteride for hair loss?
Three key clinical studies determined the effectiveness of finasteride for hair loss in men. Two clinical trials focused on men losing hair at the crown (top) of the head, and one study concentrated on men with a receding hairline.
Based on hair count, 2 years of finasteride treatment prevented additional hair loss in 83% of men with crown hair loss. And 1 year of finasteride therapy blocked further hair loss in 70% of men with a receding hairline.
As for finasteride in women, a small 2006 clinical trial showed that 62% of premenopausal women have better hair density after 1 year of combining daily finasteride 2.5 mg with a drospirenone-containing birth control pill. Drospirenone is a human-made version of the naturally-occurring progesterone sex hormone.
In a 2014 clinical trial, approximately 82% of premenopausal and postmenopausal women showed an improvement in hair thickness. Plus, about 69% of them experienced better hair density. These study participants took finasteride 1.25 mg every day for 3 years.
Can you still go bald on finasteride?
The short answer is yes.
In general, finasteride is more effective if you start taking it soon after you notice hair loss. In fact, clinical studies suggested that men will most likely benefit from finasteride within 5 years of first experiencing hair loss — with a bald spot of less than 10 cm (4 inches).
Once you start taking finasteride, be patient. It might take at least 3 months to work. If you don’t notice any benefit by then, talk with your healthcare provider. They can discuss other hair loss treatment options with you.
If finasteride is working for you, you will need to continue taking this medication every day to prevent further hair loss. If you stop taking finasteride, you will experience hair loss again.
What dosage of finasteride works for hair loss in women?
Finasteride for hair loss in women is an off-label use. This means the FDA doesn’t provide standard dose recommendations for women taking it. However, several studies suggest that finasteride at 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg per day may help women with hair loss.
But experts don’t typically recommend finasteride as the initial go-to option for women with hair loss. Instead, experts prefer Rogaine (minoxidil) 2%, which is an over-the-counter (OTC) product that is applied to the part of the scalp that is affected by hair loss.
Do higher doses work better for hair loss in women?
If 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg a day works, is 5 mg a day better? Not necessarily.
A number of studies have shown that taking 5 mg of finasteride a day improved hair density and thickness. But the women in the studies had several unwanted side effects, including:
Headaches
Dizziness
Abnormal menstrual periods
Breast tenderness
Excess body hair growth
But most of these side effects were mild and faded over time.
Lower doses of 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg per day of finasteride seem to achieve similar results as 5 mg per day for women — and with fewer side effects. But more research is needed to determine the best treatment dose and schedule.
Can you drink alcohol while taking Finasteride?
In short, avoid heavy alcohol drinking. Heavy alcohol drinking is considered having over 3 drinks per day for more than 4 days out of the week.
Propecia’s manufacturer — Merck — didn’t specifically mention any interactions between this medication and alcohol. But a 2009 study suggested that heavy alcohol drinking can raise the risk of prostate cancer in men.
Should I take finasteride?
Finasteride is an FDA-approved treatment option for men with male pattern hair loss. Finasteride may also be a useful option in women who do not intend to get pregnant, especially those who didn’t find Rogaine to be effective.
If you’re interested in trying finasteride, speak with your healthcare provider.
The bottom line
If you are experiencing hair loss, there are some treatment options that might help. Healthcare experts recommend women experiencing hair loss to try Rogaine. But if you don’t notice any benefit, your healthcare provider might recommend finasteride for hair loss.
Although finasteride has been shown to be an effective treatment in men, it can also be considered for hair loss in women. While it does help improve hair thickness, finasteride has to be taken long-term for it to work. It may also lead to unpleasant side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider to determine which option is right for you.
Advertisement
Access this offer
Say hello to thicker, fuller hair
Regrow thicker hair in 3-6 months.* (Disclaimer:
Based on studies of topical and oral minoxidil)
No office or pharmacy visits required.
Personalized treatment options in just a few clicks.
References
Al Aboud, AM., et al. (2021). Alopecia. StatPearls Publishing.
American Academy of Dermatology Association. (2022). Hair loss: overview.
Endocrine Society. (2022). Reproductive hormones.
Food and Drug Administration. (2019). Information about drospirenone.
Iamsumang, W., et al. (2020). Finasteride and its potential for the treatment of female pattern hair loss: evidence to date. Drug Design, Development and Therapy.
Iorizzo, M., et al. (2006). Finasteride treatment of female pattern hair loss. Archives of Dermatology.
MedlinePlus. (2022). Aging changes in hair and nails.
MedlinePlus. (2020). Androgenetic alopecia.
Merck Sharp & Dohme. (2021). Propecia [prescribing information].
Oliveira-Soares, R., et al. (2018). Adverse effects with finasteride 5 mg/day for patterned hair loss in premenopausal women. International Journal of Trichology.
Phillips, TG., et al. (2017). Hair loss: common causes and treatment. American Family Physician.
Shapiro, J., et al. (2003). Use of finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia (male pattern hair loss). Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings.
Skow, DT., et al. (1999). Medical treatments for balding in men. American Family Physician.
Thiedke, CC. (2003). Alopecia in women. American Family Physician.
Zhihong, G., et. al. (2009). Alcohol consumption, finasteride and prostate cancer risk: Results from the prostate cancer prevention trial. Cancer.
Was this page helpful?
Related Articles
Browse medications
View AllResearch prescriptions and over-the-counter medications from A to Z, compare drug prices, and start saving.